ShardPreference 源码分析
使用了很多,但都没具体分析过。现在来分析一下 ShardPreference 的源码。
挖个坑,可能后续会更新 mmkv 系列,用来做个对比。
SharedPreferences 接口
首先我们先看看我们平时如何使用:
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(){
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
val sp = getSharedPreferences("Heyan", MODE_PRIVATE)
}
}
这里 sp 是一个 SharedPreferences 类型的接口,先来看看该接口:
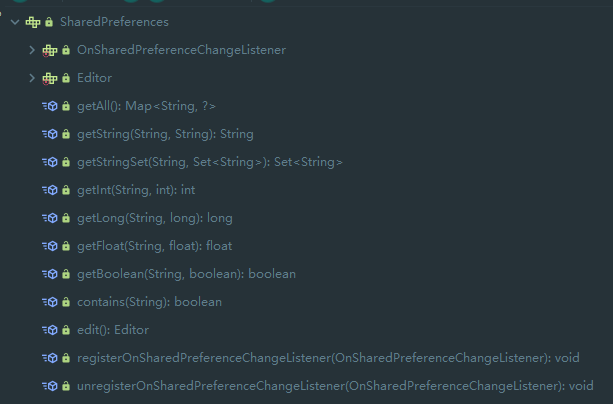
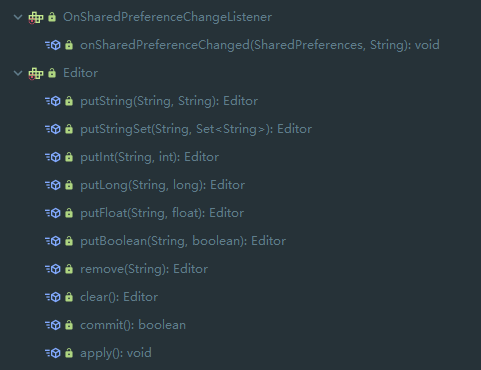
有两个内部类,OnShardPreferChangeListener 和 Editor,其定义如下:
其实现类等等在分析,先来看看 我们获取该接口的过程。
ContextImpl#getSharedPreferences
Activity 的 getSharedPreferences 方法,实际上会调用 ContextWrapper 的同名方法,因为是装饰类。最终会来到 ContextImpl 的该方法,如下:
class ContextImpl extends Context {
// 这里省略和 SharedPreferences 无关的内容
// ArrayMap 数据结构后面文章会分析,这里暂时理解为 HashMap 即可
// 包名到 ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> 的映射
private static ArrayMap<String, ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl>> sSharedPrefsCache;
// 路径到 File 对象的缓存
private ArrayMap<String, File> mSharedPrefsPaths;
@Override
public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(String name, int mode) {
// At least one application in the world actually passes in a null
// name. This happened to work because when we generated the file name
// we would stringify it to "null.xml". Nice.
// 居然有名称为 null 的 app,笑死。
if (mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion <
Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
if (name == null) {
name = "null";
}
}
File file;
// 同步锁,这里主要是要确保 mSharedPrefsPaths 的线程安全
synchronized (ContextImpl.class) {
if (mSharedPrefsPaths == null) {
mSharedPrefsPaths = new ArrayMap<>();
}
file = mSharedPrefsPaths.get(name);
if (file == null) {
file = getSharedPreferencesPath(name);
mSharedPrefsPaths.put(name, file);
}
}
// 获取到 file 后调用另一个方法
return getSharedPreferences(file, mode);
}
@Override
public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(File file, int mode) {
SharedPreferencesImpl sp;
// 同步锁,这里主要是对 sSharedPrefsCache 容器加锁(在 getSharedPreferencesCacheLocked() 方法里)
synchronized (ContextImpl.class) {
// 调用 getSharedPreferencesCacheLocked() 方法获取对应 ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl>
// 这里名字最后加了 Locked 应该是代表必须加锁才能调用
final ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> cache = getSharedPreferencesCacheLocked();
sp = cache.get(file);
if (sp == null) {
// 检查 mode
checkMode(mode);
// 安卓 o 之后会增加一个 存储 锁定状态,这里进行判断。
if (getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
if (isCredentialProtectedStorage()
&& !getSystemService(UserManager.class)
.isUserUnlockingOrUnlocked(UserHandle.myUserId())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("SharedPreferences in credential encrypted "
+ "storage are not available until after user is unlocked");
}
}
// 实例化一个 SharedPreferencesImpl,放入缓存
sp = new SharedPreferencesImpl(file, mode);
cache.put(file, sp);
return sp;
}
}
// 如果为 多进程 访问模式,或者安卓 3 以下(这里猜测之前没考虑多进程,没有该标志位,不过安卓 3 太过久远现在不用考虑)
if ((mode & Context.MODE_MULTI_PROCESS) != 0 ||
getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {
// If somebody else (some other process) changed the prefs
// file behind our back, we reload it. This has been the
// historical (if undocumented) behavior.
sp.startReloadIfChangedUnexpectedly();
}
return sp;
}
// 获取 SharedPreferencesCach
private ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> getSharedPreferencesCacheLocked() {
// 确保 sSharedPrefsCache 不为 null
if (sSharedPrefsCache == null) {
sSharedPrefsCache = new ArrayMap<>();
}
// 使用包名作为 key
final String packageName = getPackageName();
ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> packagePrefs = sSharedPrefsCache.get(packageName);
if (packagePrefs == null) {
packagePrefs = new ArrayMap<>();
sSharedPrefsCache.put(packageName, packagePrefs);
}
return packagePrefs;
}
// 安卓 N 之后不在支持 MODE_WORLD_READABLE 和 MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE 的 Flag
// 实际上就是不允许其他 app 读写你的 sp
private void checkMode(int mode) {
if (getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
if ((mode & MODE_WORLD_READABLE) != 0) {
throw new SecurityException("MODE_WORLD_READABLE no longer supported");
}
if ((mode & MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE) != 0) {
throw new SecurityException("MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE no longer supported");
}
}
}
}
SharedPreferencesImpl
接下来 来到 SharedPreferencesImpl 类。该类比较复杂这里一个方法一个方法看,先看看构造方法:
final class SharedPreferencesImpl implements SharedPreferences {
private final File mFile;
private final File mBackupFile;
private final int mMode;
private final Object mLock = new Object();
// 以下变量需要用 mLock 同步锁控制
private boolean mLoaded = false;
private Map<String, Object> mMap;
private Throwable mThrowable;
SharedPreferencesImpl(File file, int mode) {
mFile = file;
mBackupFile = makeBackupFile(file);
mMode = mode;
mLoaded = false;
mMap = null;
mThrowable = null;
startLoadFromDisk();
}
// 设置备份文件
static File makeBackupFile(File prefsFile) {
return new File(prefsFile.getPath() + ".bak");
}
}
构造方法里调用了 startLoadFromDisk 方法,接下来来看看该方法:
final class SharedPreferencesImpl implements SharedPreferences {
private void startLoadFromDisk() {
// 加锁赋值 mLoaded
synchronized (mLock) {
mLoaded = false;
}
// 开线程,调用 loadFromDisk
new Thread("SharedPreferencesImpl-load") {
public void run() {
loadFromDisk();
}
}.start();
}
}
异步调用 loadFromDisk,来看看 loadFromDisk:
final class SharedPreferencesImpl implements SharedPreferences {
private void loadFromDisk() {
// 加锁
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mLoaded) {
return;
}
// 如果 备份文件存在,则替换
if (mBackupFile.exists()) {
mFile.delete();
mBackupFile.renameTo(mFile);
}
}
// Debugging
if (mFile.exists() && !mFile.canRead()) {
Log.w(TAG, "Attempt to read preferences file " + mFile + " without permission");
}
// 这里开始是从文件读数据并解析
Map<String, Object> map = null;
StructStat stat = null;
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath());
if (mFile.canRead()) {
BufferedInputStream str = null;
try {
str = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(mFile), 16 * 1024);
// 解析
map = (Map<String, Object>) XmlUtils.readMapXml(str);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Cannot read " + mFile.getAbsolutePath(), e);
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(str);
}
}
} catch (ErrnoException e) {
// An errno exception means the stat failed. Treat as empty/non-existing by
// ignoring.
} catch (Throwable t) {
thrown = t;
}
// 上面是把数据读到局部变量 map 中
// 以下是赋值给 mMap,主要是对 mMap 加锁
synchronized (mLock) {
mLoaded = true;
mThrowable = thrown;
// It's important that we always signal waiters, even if we'll make
// them fail with an exception. The try-finally is pretty wide, but
// better safe than sorry.
try {
if (thrown == null) {
if (map != null) {
mMap = map;
mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtim;
mStatSize = stat.st_size;
} else {
mMap = new HashMap<>();
}
}
// In case of a thrown exception, we retain the old map. That allows
// any open editors to commit and store updates.
} catch (Throwable t) {
mThrowable = t;
} finally {
// 这里需要唤醒等待读锁的线程
mLock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
接下来看看数据读取的方法,以 getSring 为例:
final class SharedPreferencesImpl implements SharedPreferences {
public String getString(String key, @Nullable String defValue) {
// 同步锁
synchronized (mLock) {
// 等待 loaded 锁
awaitLoadedLocked();
// 从缓存拿
String v = (String)mMap.get(key);
// 如果为 null 就返回 defValue
return v != null ? v : defValue;
}
}
private void awaitLoadedLocked() {
if (!mLoaded) {
// Raise an explicit StrictMode onReadFromDisk for this
// thread, since the real read will be in a different
// thread and otherwise ignored by StrictMode.
BlockGuard.getThreadPolicy().onReadFromDisk();
}
// 死循环 wait
while (!mLoaded) {
try {
// 这里 wait 后,在 loadFromDisk 方法中会被唤醒
mLock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException unused) {
}
}
if (mThrowable != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(mThrowable);
}
}
}
接下来分析写入:
Editor
首先我们需要获取一个 Editor:
final class SharedPreferencesImpl implements SharedPreferences {
@Override
public Editor edit() {
// TODO: remove the need to call awaitLoadedLocked() when
// requesting an editor. will require some work on the
// Editor, but then we should be able to do:
//
// context.getSharedPreferences(..).edit().putString(..).apply()
//
// ... all without blocking.
// 等待 loaded 锁
synchronized (mLock) {
awaitLoadedLocked();
}
// 返回一个 EditorImpl 对象
return new EditorImpl();
}
}
之前我们看过 Editor 接口,这里直接看实现:
public final class EditorImpl implements Editor {
// 编辑锁
private final Object mEditorLock = new Object();
// 以下变量会受到 mEditorLock 控制
// Modifier 对象
@GuardedBy("mEditorLock")
private final Map<String, Object> mModified = new HashMap<>();
// 是否 清除
@GuardedBy("mEditorLock")
private boolean mClear = false;
// 以 putString 为例,其他类似
@Override
public Editor putString(String key, @Nullable String value) {
// 使用 EditorLock 将写入数据放进 mModified
synchronized (mEditorLock) {
mModified.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}
// 删除
@Override
public Editor remove(String key) {
synchronized (mEditorLock) {
// 这里放入 this,重点,考试要考的(后面提交的时候需要处理)
mModified.put(key, this);
return this;
}
}
// 清除
@Override
public Editor clear() {
// 直接使用标记
synchronized (mEditorLock) {
mClear = true;
return this;
}
}
}
以上还是比较好理解的,接下来分析重头戏,apply 和 commit,首先是 commit:
Commit
public final class EditorImpl implements Editor {
@Override
public boolean commit() {
long startTime = 0;
if (DEBUG) {
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
// 调用 commitToMemory 方法
MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory();
// 调用 enqueueDiskWrite 方法
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite(
mcr, null /* sync write on this thread okay */);
try {
// 等待 mcr 中的一个 CountDownLatch
mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return false;
} finally {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, mFile.getName() + ":" + mcr.memoryStateGeneration
+ " committed after " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime)
+ " ms");
}
}
// 通知
notifyListeners(mcr);
// 返回结果
return mcr.writeToDiskResult;
}
}
可以看到主要是两个方法,commitToMemory 与 enqueueDiskWrite,先来看看第一个:
commitToMemory
public final class EditorImpl implements Editor {
private MemoryCommitResult commitToMemory() {
long memoryStateGeneration;
boolean keysCleared = false;
List<String> keysModified = null;
Set<OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener> listeners = null;
Map<String, Object> mapToWriteToDisk;
// 获取 mLock 锁,主要是因为 mDiskWritesInFlight 和 mMap 要受到该锁控制
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this.mLock) {
// We optimistically don't make a deep copy until
// a memory commit comes in when we're already
// writing to disk.
// 如果其他线程在写入(持有 mMap)
// 这里计数器要等到写入到磁盘里才会减一,因此如果这里大于 0 说明有其他版本正在写入磁盘
// 写入磁盘的时候会持有已有的 mMap,因此这里需要进行克隆
if (mDiskWritesInFlight > 0) {
// We can't modify our mMap as a currently
// in-flight write owns it. Clone it before
// modifying it.
// noinspection unchecked
// 进行一个隆的克
mMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(mMap);
}
// 赋值,以后的操作对 mapToWriteToDisk 进行
mapToWriteToDisk = mMap;
// 写入计数器 ++
mDiskWritesInFlight++;
// 监听器预操作
boolean hasListeners = mListeners.size() > 0;
if (hasListeners) {
keysModified = new ArrayList<String>();
listeners = new HashSet<OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener>(mListeners.keySet());
}
// 获取 mEditorLock 锁,主要是 mClear 和 mModified 受到该锁控制
synchronized (mEditorLock) {
// 标记是否有更改
boolean changesMade = false;
// clear 操作,直接 clear
if (mClear) {
if (!mapToWriteToDisk.isEmpty()) {
// changesMade 需要真正有删除才会为 true
changesMade = true;
mapToWriteToDisk.clear();
}
keysCleared = true;
mClear = false;
}
// 遍历 mModified
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> e : mModified.entrySet()) {
String k = e.getKey();
Object v = e.getValue();
// "this" is the magic value for a removal mutation. In addition,
// setting a value to "null" for a given key is specified to be
// equivalent to calling remove on that key.
// 这里 v 为 this 和 为 null 都表示 remove
if (v == this || v == null) {
if (!mapToWriteToDisk.containsKey(k)) {
// 没数据 continue
continue;
}
mapToWriteToDisk.remove(k);
} else {
if (mapToWriteToDisk.containsKey(k)) {
Object existingValue = mapToWriteToDisk.get(k);
if (existingValue != null && existingValue.equals(v)) {
// 数据一样 continue
continue;
}
}
// put
mapToWriteToDisk.put(k, v);
}
// 如果没 continue 说明肯定真正修改了数据
changesMade = true;
if (hasListeners) {
// 将需要通知监听器的 key 放入 keysModified
keysModified.add(k);
}
}
// 清空当前 缓冲区
mModified.clear();
// 如果修改了,更新版本
if (changesMade) {
mCurrentMemoryStateGeneration++;
}
// 修改版本
memoryStateGeneration = mCurrentMemoryStateGeneration;
}
}
// 返回结果实体
return new MemoryCommitResult(memoryStateGeneration, keysCleared, keysModified,
listeners, mapToWriteToDisk);
}
}
还是比较好理解的,接下来是 enqueueDiskWrite
enqueueDiskWrite
public final class EditorImpl implements Editor {
private void enqueueDiskWrite(final MemoryCommitResult mcr,
final Runnable postWriteRunnable) {
// 是否是同步请求
final boolean isFromSyncCommit = (postWriteRunnable == null);
// 构造 runnable
final Runnable writeToDiskRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 获取 mWritingToDiskLock 锁后调用 writeToFile 写入文件
synchronized (mWritingToDiskLock) {
writeToFile(mcr, isFromSyncCommit);
}
// 获取 mLock 锁后将计数器 -1
synchronized (mLock) {
mDiskWritesInFlight--;
}
// 回调
if (postWriteRunnable != null) {
postWriteRunnable.run();
}
}
};
// Typical #commit() path with fewer allocations, doing a write on
// the current thread.
// 如果是同步的,不用开线程,直接 run
if (isFromSyncCommit) {
boolean wasEmpty = false;
// 毕竟 mDiskWritesInFlight 要受到 mLock 锁控制
synchronized (mLock) {
// 如果只有一个版本,则直接运行
wasEmpty = mDiskWritesInFlight == 1;
}
if (wasEmpty) {
// 直接运行并返回
writeToDiskRunnable.run();
return;
}
}
// 加入 QueuedWork
// 如果是同步,则不 delay, 否则会进行 180 ms 的 delay
QueuedWork.queue(writeToDiskRunnable, !isFromSyncCommit);
}
}
这里调用了 writeToFile 方法,这里具体写入不给出,只给出部分代码:
writeToFile
final class SharedPreferencesImpl implements SharedPreferences {
private void writeToFile(MemoryCommitResult mcr, boolean isFromSyncCommit){
// 省略部分代码
boolean fileExists = mFile.exists();
// 如果文件已 存在
if (fileExists) {
boolean needsWrite = false;
// Only need to write if the disk state is older than this commit
// 如果这次提交版本号大于文件的版本号
if (mDiskStateGeneration < mcr.memoryStateGeneration) {
// 同步写都直接写
if (isFromSyncCommit) {
needsWrite = true;
} else {
// 异步写则交给当前 MemoryCommitResult 的最新版本
// mCurrentMemoryStateGeneration 变量需要受到 mLock 控制
synchronized (mLock) {
// No need to persist intermediate states. Just wait for the latest state to
// be persisted.
if (mCurrentMemoryStateGeneration == mcr.memoryStateGeneration) {
needsWrite = true;
}
}
}
}
// 如果不需要写直接给结果(通过 mcr 给结果 之后会分析)
if (!needsWrite) {
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false, true);
return;
}
boolean backupFileExists = mBackupFile.exists();
// 如果备份文件不存在
if (!backupFileExists) {
// 将文件命名为备份文件,之后如果有读取,走备份文件
if (!mFile.renameTo(mBackupFile)) {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't rename file " + mFile
+ " to backup file " + mBackupFile);
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false, false);
return;
}
} else {
// 删除文件,不需要备份文件,直接重新写
mFile.delete();
}
}
try{
// 写入 代码省略
// 通知结果
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(true, true);
return;
}catch(Exception e){
// 省略多种异常处理
}
// 到这里说明有异常
// 删除文件 然后通知结果错误
if (mFile.exists()) {
if (!mFile.delete()) {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't clean up partially-written file " + mFile);
}
}
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false, false);
}
}
接下来来看看这个 mcr 也就是 MemoryCommitResult 对象:
private static class MemoryCommitResult {
final long memoryStateGeneration;
final boolean keysCleared;
@Nullable final List<String> keysModified;
@Nullable final Set<OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener> listeners;
final Map<String, Object> mapToWriteToDisk;
final CountDownLatch writtenToDiskLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
@GuardedBy("mWritingToDiskLock")
volatile boolean writeToDiskResult = false;
boolean wasWritten = false;
private MemoryCommitResult(long memoryStateGeneration, boolean keysCleared,
@Nullable List<String> keysModified,
@Nullable Set<OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener> listeners,
Map<String, Object> mapToWriteToDisk) {
this.memoryStateGeneration = memoryStateGeneration;
this.keysCleared = keysCleared;
this.keysModified = keysModified;
this.listeners = listeners;
this.mapToWriteToDisk = mapToWriteToDisk;
}
void setDiskWriteResult(boolean wasWritten, boolean result) {
this.wasWritten = wasWritten;
writeToDiskResult = result;
// 通知结果后,会将 CountDownLatch 进行一个 countDown
// 通知操作完成
writtenToDiskLatch.countDown();
}
}
然后是 Apply 过程:
public final class EditorImpl implements Editor {
@Override
public void apply() {
final long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 还是调用 commitToMemory()
final MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory();
final Runnable awaitCommit = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 回调里等 mcr 里的 writtenToDiskLatch
mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
if (DEBUG && mcr.wasWritten) {
Log.d(TAG, mFile.getName() + ":" + mcr.memoryStateGeneration
+ " applied after " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime)
+ " ms");
}
}
};
// 添加一个 finisher,主要是埋炸弹,要确保 QueuedWork 里的任务要等 writtenToDiskLatch count 后才能执行下一个任务
QueuedWork.addFinisher(awaitCommit);
// 真正运行 runnable
Runnable postWriteRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行完毕了,直接等 writtenToDiskLatch
awaitCommit.run();
// 因为已经有等待了,这里直接 remove 调之前的炸弹
QueuedWork.removeFinisher(awaitCommit);
}
};
// 调用 enqueueDiskWrite,这里 postWriteRunnable 不为空
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite(mcr, postWriteRunnable);
// Okay to notify the listeners before it's hit disk
// because the listeners should always get the same
// SharedPreferences instance back, which has the
// changes reflected in memory.
// 直接回调监听器,因为监听的是内存,文件写入是否成功不关心。
notifyListeners(mcr);
}
}